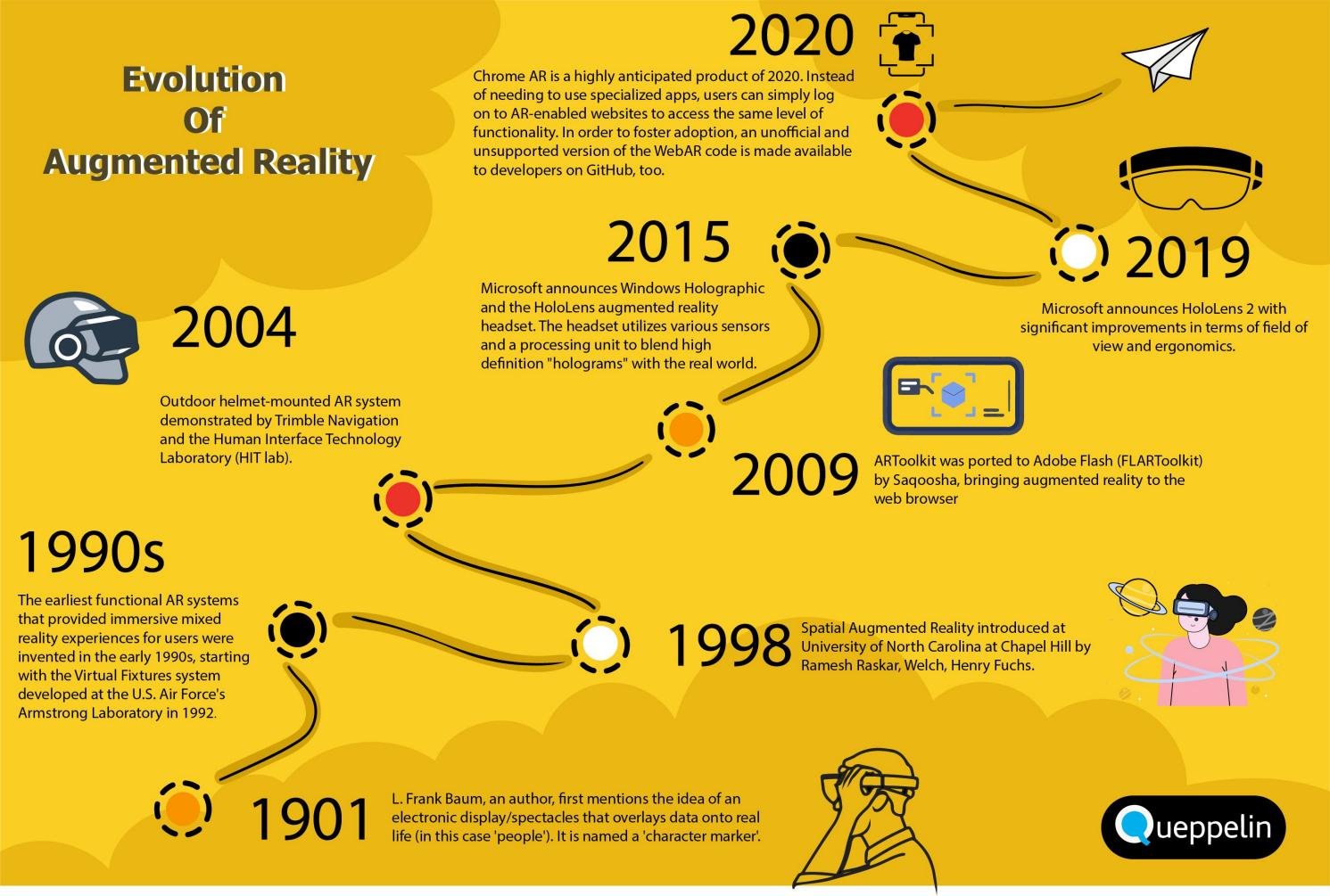
The Evolution of Augmented Reality and Its Impact on Industries
The evolution of augmented reality is rapidly transforming industries, driving innovation and revolutionizing how we interact with the world around us. From simple overlays to complex holographic experiences, AR is progressively altering numerous sectors, creating new possibilities and redefining traditional approaches. This article delves into the captivating journey of AR evolution, exploring its remarkable impact on various industries, highlighting key trends, applications, and the exciting future that lies ahead. This comprehensive exploration will also address challenges faced by businesses hoping to integrate AR and offer solutions for the future.
1. Early Stages and Initial Applications
1.1 The Genesis of Augmented Reality
Early augmented reality experiments focused on overlaying digital information onto the physical world, primarily through computer vision and graphics. These initial applications were often limited by computational power and display technology, with early examples including simple visual overlays on simple devices.
1.2 Pioneering Applications in Specific Sectors
Initial use cases were often niche, found in specialized fields. For instance, AR began to appear in training simulations for professionals in sectors like aerospace and military training. These early projects emphasized practical application of AR technology to specific problems, often tailored for a very particular audience.
1.3 The Rise of Mobile AR
The emergence of smartphones and tablets revolutionized AR development. Increased computing power, user-friendly interfaces, and wider device accessibility enabled more widespread and interactive AR experiences.
1.4 The Limitations of Early Systems
Despite these advancements, early augmented reality systems suffered from challenges like limited accuracy of tracking, poor graphics, and sometimes uncomfortable user interfaces.
1.5 Early Acceptance by Consumers
Despite these hurdles, some early mobile AR applications started generating consumer interest, foreshadowing the potential of the technology and paving the way for the next stage of evolution.
2. The Advancement of Computing Power
2.1 Improved Processing Capabilities
Advancements in computing power are pivotal to AR evolution. More powerful processors enable more complex algorithms, higher-resolution graphics, and improved interaction with augmented environments.
2.2 Real-Time Tracking Improvements
Accurate, real-time tracking is critical for seamless integration of digital elements with the real world. Advances in sensor technology, particularly in smartphone cameras, significantly enhanced the precision of AR tracking.
2.3 Sophisticated Rendering Technologies
Enhanced rendering technologies allow for more realistic and visually appealing AR experiences. Improvements in graphics processing units (GPUs) translate to higher frame rates and better image quality, leading to more immersive interactions.
2.4 Accessibility and Affordability
Improved affordability and wider accessibility of AR devices are crucial. These developments have lowered the barrier to entry and enabled wider adoption across various sectors.
2.5 Augmented Reality in the Enterprise
Increased interest from businesses in AR for training and productivity applications has been a key driver for further developments.
3. Expanding Applications Across Industries
3.1 Retail and E-commerce Applications
AR technology is transforming the retail and e-commerce landscape. Retailers can offer virtual try-on experiences, interactive product demonstrations, and personalized shopping experiences.
3.2 AR in Healthcare
Augmented reality plays a transformative role in healthcare, aiding in surgery, training, and diagnostics. Surgical procedures can be aided by AR overlays providing real-time guidance, improving precision and reducing errors. Medical training programs can use AR to create interactive and realistic scenarios.
3.3 The Educational Landscape
AR provides engaging and interactive educational experiences. Students can access 3D models, simulations, and virtual tours in various subjects, enhancing understanding and retention.
3.4 Gaming and Entertainment
AR is expanding into the gaming and entertainment industry with immersive experiences and interactive games that blend digital elements with the real world.
3.5 Future Possibilities: Merging with Other Technologies
AR is becoming increasingly integrated with other technologies, like AI and machine learning, expanding its capabilities and creating new opportunities for innovation.
4. Challenges and Opportunities
4.1 Cost of Implementation
Businesses may encounter costs associated with implementing AR technology, including software, hardware, and personnel training. This can be a barrier for smaller businesses, but the potential return on investment is often substantial.
4.2 The Need for Specialized Skills
Integrating and utilizing AR effectively often requires specialized skills, creating a demand for professionals with expertise in AR development.
4.3 Addressing Privacy Concerns
Privacy concerns surrounding data collection and usage within AR systems need to be addressed for responsible development and adoption.
4.4 Overcoming User Experience Barriers
Creating an intuitive user experience is essential to ensure widespread AR adoption. Design that focuses on ease of use and a natural integration with existing workflows is crucial.
4.5 Technological Advancements
Further advancements in areas like computer vision, graphics processing, and sensor technology will drive the continued evolution of AR in the future
Related Post : How IoT Devices Are Transforming Everyday Lives
5. The Future of Augmented Reality
5.1 The Rise of Immersive Experiences
The future of AR is driven by increasingly immersive experiences, blending digital and physical realities to provide more natural and interactive interfaces.
5.2 AR's Role in Remote Work
AR can play a vital role in remote work, facilitating collaboration between geographically dispersed teams, providing real-time support, and creating a more engaging virtual environment.
5.3 AR in Manufacturing
AR has the potential to streamline and enhance manufacturing processes, enabling remote assistance, guiding technicians in maintenance or repairs, and augmenting the efficiency of assembly line operations.
5.4 AI-Powered AR
The integration of AI is expected to significantly shape the future of AR, providing more intelligent and responsive experiences, enabling personalization, and driving improved accuracy in real-time interactions.
5.5 The Importance of Research and Development
Continued research and development in areas such as improved user experiences, cost-effectiveness of devices, and integration with other technologies are crucial to expanding the applications of AR.
In conclusion, the evolution of augmented reality is reshaping numerous industries, from retail and healthcare to gaming and education. As AR technology continues to mature, its impact will only increase, creating new possibilities and challenges. To stay ahead of the curve, businesses must understand the transformative potential of AR and actively explore its applications in their respective sectors. Further research and development in areas such as improved user experiences and more affordable devices are critical to fostering wider adoption and innovation. By embracing AR, businesses can unlock unprecedented opportunities for growth and efficiency in the years to come. Explore the latest AR advancements by visiting our website!
Share this content:












Post Comment