How Data Privacy Laws Are Reshaping the Future of Technology

Data privacy laws are profoundly reshaping the future of technology, forcing a paradigm shift in how companies collect, use, and manage user data. This evolution is driven by growing concerns about user privacy and the increasing potential for misuse of personal information. The digital age has created an unprecedented amount of data, and with it, new challenges around safeguarding user information. This article explores how global data privacy laws are transforming the tech industry, highlighting the challenges and opportunities. We’ll delve into the impact of specific regulations, discuss the ethical considerations involved, and outline the necessary adaptations for technology companies. This comprehensive guide will explain how to remain compliant, protect user rights, and leverage innovation responsibly.
1. The Global Landscape of Data Privacy Laws
1.1. Key Regulations and Their Impact
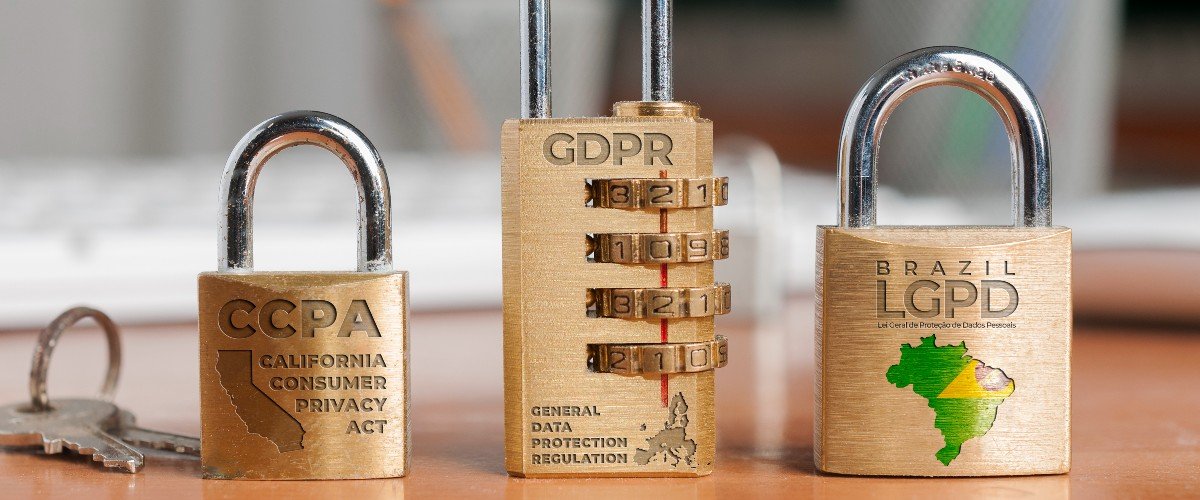
Data privacy laws are no longer a niche concern; they’re a global imperative. Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the US are not just guidelines—they are legal mandates that significantly impact how organizations worldwide handle user data. These laws affect everything from the way companies collect data to how they store and process it. Consider the implications of breaches – potential reputational damage, legal penalties, and significant financial losses. These consequences drive a critical need for meticulous data protection practices. For instance, companies must now ensure compliance by obtaining informed consent from users before collecting personal data, and establish clear procedures for data deletion and access requests. Many organizations are finding that adapting to these regulations requires significant investments in technology and human capital.
1.2. The Rise of International Cooperation
The global nature of data flows necessitates cross-border cooperation. Companies operating across different jurisdictions need sophisticated strategies for complying with various regional standards. This is forcing a global approach to data protection where harmonization is gradually emerging, although the specifics still vary by region. The evolving international landscape requires technology companies to demonstrate a commitment to protecting user privacy in accordance with a growing number of international and regional data privacy laws. For instance, international trade agreements now often include provisions addressing data privacy.
2. The Ethical Dimensions of Data Privacy
2.1. Balancing Innovation and User Rights
Data privacy laws often demand a careful balancing act: allowing innovation while protecting the fundamental rights of individuals. The very nature of technological advancement sometimes leads to new data collection possibilities, creating a constant tension. In this case, it is vital that technology companies implement ethical frameworks that guide their data usage. Companies need to articulate clear and transparent data handling policies, ensuring user awareness and engagement. Companies should clearly communicate their data collection, usage, and protection policies. For example, clear policies explaining how data is collected, what it’s used for, and what protections are in place can significantly enhance public trust.
2.2. The Role of User Consent and Transparency
In the realm of data protection, informed consent and transparency are paramount. Users need clear and understandable explanations of how their data is collected, used, and protected. The process needs to be clear to the user at each step. Providing clear, comprehensive information minimizes the likelihood of misunderstandings. Data privacy laws mandate companies to secure user consent to collect, use, and share personal information. Transparency and accountability are cornerstones of data privacy initiatives. Providing users with tools for monitoring their data and requesting corrections or deletions also plays a vital role.
3. The Practical Implications for Technology Companies
3.1. Adapting to Evolving Regulations
Navigating the complex world of data privacy laws requires constant adaptation and vigilance. Companies must carefully monitor updates and changes to legislation and ensure their policies and practices remain compliant. This necessitates ongoing monitoring and adjustment strategies. For example, the constant evolution of data privacy laws necessitates regular reviews of existing policies and systems. Businesses must remain informed about updates to regulations such as GDPR and CCPA to avoid non-compliance issues.
3.2. Investing in Data Protection Technologies
Maintaining data security and privacy isn’t just a matter of policy; it demands robust technological infrastructure. Companies must invest in tools and systems to encrypt data, monitor for breaches, and enable data deletion and access requests. Robust data security infrastructure is needed to deter unauthorized access and protect sensitive user information. For example, end-to-end encryption can enhance the safety of user data during transmission and storage. Effective data protection technologies are critical in the digital age, especially as cyber threats become more sophisticated.
4. The Future of Technology in a Data-Driven World
4.1. Promoting Innovation with Responsibility
Data privacy laws don’t stifle innovation; rather, they channel it in a more ethical and user-centric direction. The focus shifts to developing technologies that respect user privacy while also delivering valuable services. Data privacy drives new approaches to development, especially in fields where data security is critical. In this instance, the development of privacy-preserving technologies like differential privacy, federated learning, and homomorphic encryption is crucial. These technologies allow for data analysis without compromising user privacy, pushing boundaries in how we collect and utilize data for research and development.
4.2. The Role of Ethical Frameworks
Companies should adopt comprehensive ethical frameworks for data handling to ensure long-term viability in a regulated environment. These frameworks provide a framework for addressing ethical dilemmas associated with the development and deployment of new technologies. Companies are creating comprehensive ethical frameworks, outlining policies for responsible data collection, usage, and storage. This is an important element of ongoing innovation that reflects a modern and well-regulated approach to data handling.
Related Post : Cloud Computing in 2024 Latest Advancements and Applications
5. The Impact of Data Privacy on Industries
5.1. The Evolving E-commerce Landscape
The e-commerce sector is particularly affected by the need to comply with data privacy laws. Businesses must now adhere to strict regulations around user data collection, consent, and storage. Businesses need to ensure that online platforms are well-protected, with security protocols consistently updated. For instance, online retailers must provide clear and comprehensive privacy policies detailing how customer data is used and shared, ensuring trust and transparency.
5.2. The Importance of Data Security in Healthcare
The healthcare sector’s handling of sensitive patient data is highly regulated. Protecting patient confidentiality is paramount. Data privacy laws help create a trusted system for the exchange and storage of data, improving the healthcare experience and patient protection. For example, ensuring compliance with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) regulations is critical for healthcare providers and institutions.
5.3. Financial Institutions: Balancing Security and Service
Financial institutions are under immense pressure to safeguard customer data. Striking a balance between providing essential financial services and meeting stringent data protection standards is essential. For example, implementing advanced security measures, conducting regular audits, and enhancing communication with customers are critical for building trust and ensuring compliance.
5.4. Data Privacy in Educational Institutions
Educational institutions must adhere to stringent guidelines for safeguarding student data. Data privacy regulations are crucial to ensuring protection for the future generation, maintaining a safe environment, and complying with local regulations. For example, school districts need to comply with guidelines like FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act) to ensure the security and privacy of student records.
5.5. Data Privacy in the Media
The media industry often deals with sensitive data, including personal information of public figures. Data privacy rules are important for protecting the individuals involved and ensuring ethical reporting. For example, media organizations need to be conscious of the types of data they collect and how they use it to maintain trust with audiences and comply with the law. This means adhering to stringent guidelines concerning data protection and transparency in data handling practices in the media sector in compliance with local regulations.
In conclusion, data privacy laws are fundamentally reshaping the future of technology, driving innovation while simultaneously demanding ethical considerations. Companies must prioritize data protection and user rights to foster trust, compliance, and sustainable growth. The future of tech depends on responsible data handling, prioritizing user privacy alongside innovation. This means continuous education, adaptation to evolving regulations, and prioritizing user well-being. To understand the evolving landscape, ongoing vigilance and updated knowledge are crucial. By embracing these principles, the tech industry can ensure a future where data privacy and technological advancement coexist harmoniously. Dive deeper into the nuances of data privacy and the future of technology by visiting [link to relevant resource or company page].
Share this content:













Post Comment